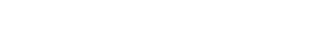
Allergic reactions can happen to anyone, anywhere, at home, at work, or out and about. They can range from mild irritation to life-threatening emergencies, making it essential to recognise allergic reaction symptoms early and respond appropriately. Knowing what to look for and how to act can save lives.
This guide covers everything you need to know about allergic reactions, from causes and stages to recognising severe reactions and knowing when to seek emergency help. By the end, you’ll feel prepared and confident to respond safely.
Allergic Reaction Symptoms: Essential Knowledge For Everyone
Allergic reactions occur when your immune system mistakenly identifies a harmless substance, called an allergen, as a threat. In response, your body releases chemicals, such as histamine, which can cause symptoms such as swelling, itching, sneezing, or hives. Reactions can range from mild irritation to severe anaphylaxis, a medical emergency.
At Medic 365, we provide practical first aid training, including first aid courses in Milton Keynes, teaching how to recognise and manage allergic reactions effectively. Understanding allergic reaction symptoms is a key part of first aid, and learning the basics can make all the difference in an emergency. For a broader overview, check out our guide on First Aid Basics.
Here’s what this guide will cover:
- What Causes Allergic Reactions?
- How Long Do Allergic Reactions Take?
- Allergic Reaction Anaphylaxis Symptoms
- 5 Stages Of Allergic Reactions
- How Long Do Allergic Reactions Last
- How To Handle An Allergic Reaction
- When To Call An Ambulance For An Allergic Reaction

What Causes Allergic Reactions?
Allergic reactions occur when your immune system mistakes a normally harmless substance for a threat. This overreaction triggers the release of chemicals, like histamine, which lead to the familiar allergy symptoms.
How an allergic reaction unfolds:
- Exposure: You come into contact with an allergen, which could be pollen in the air, a peanut in your meal, or an insect sting
- Immune Response: Your body responds by producing specific antibodies to fight the perceived threat
- Chemical Release: On your next encounter with the allergen, these antibodies trigger immune cells (mast cells) to release histamine and other chemicals
- Symptoms Appear: These chemicals cause the classic signs of an allergic reaction, such as swelling, itching, sneezing, wheezing, or rashes
Common triggers include:
- Environmental: Things like pollen, dust mites, mould spores, or pet dander can provoke reactions
- Food: Peanuts, tree nuts, milk, eggs, shellfish, fish, wheat, and soy are frequent culprits
- Insect stings: Bees, wasps, and ants can trigger sudden reactions
- Medications: Certain antibiotics, aspirin, or ibuprofen may cause allergies in some people
- Other: Items like latex gloves or balloons can sometimes provoke a reaction
For a more detailed overview, you can visit the NHS advice on allergies.
How severe reactions can be:
- Mild: You might notice sneezing, itchy eyes, a runny nose, or a few hives, uncomfortable but manageable
- Severe (Anaphylaxis): Symptoms can escalate quickly, including throat tightness, difficulty breathing, dizziness, or a sudden drop in blood pressure. These situations are life-threatening and require immediate adrenaline and professional medical attention
How Long Do Allergic Reactions Take?
Allergic reactions can show up at different times depending on the person and what triggered them. Some happen almost immediately, while others may take hours or even a few days to develop. Knowing what to expect can help you act quickly and keep someone safe.
Typical timelines:
- Immediate (Minutes): Certain triggers, like food, insect stings, or things in the air, can cause reactions almost straight away. Tingling, swelling, wheezing, or hives may appear within moments
- Delayed (Hours): Sometimes, severe reactions, including anaphylaxis, don’t show up until 2–3 hours after exposure, but they can progress very quickly once they start
- Very Delayed (Days): Contact allergies, such as reactions to metals, cosmetics, or some plants, can take a few days before any rash or irritation becomes visible
Key things to keep in mind:
- Mild symptoms like itching, sneezing, or small rashes can often be treated with antihistamines. However, they shouldn’t be ignored, as they could be an early warning of a more serious reaction
- Severe reactions (Anaphylaxis) are life-threatening and require immediate adrenaline (EpiPen) and emergency medical help
- Biphasic reactions: Sometimes a second wave of symptoms can appear hours after the first. That’s why it’s important to continue monitoring the person even if they start to feel better
If you think someone is experiencing a severe allergic reaction, use their EpiPen if they have one and call emergency services straight away. Acting fast can save lives.
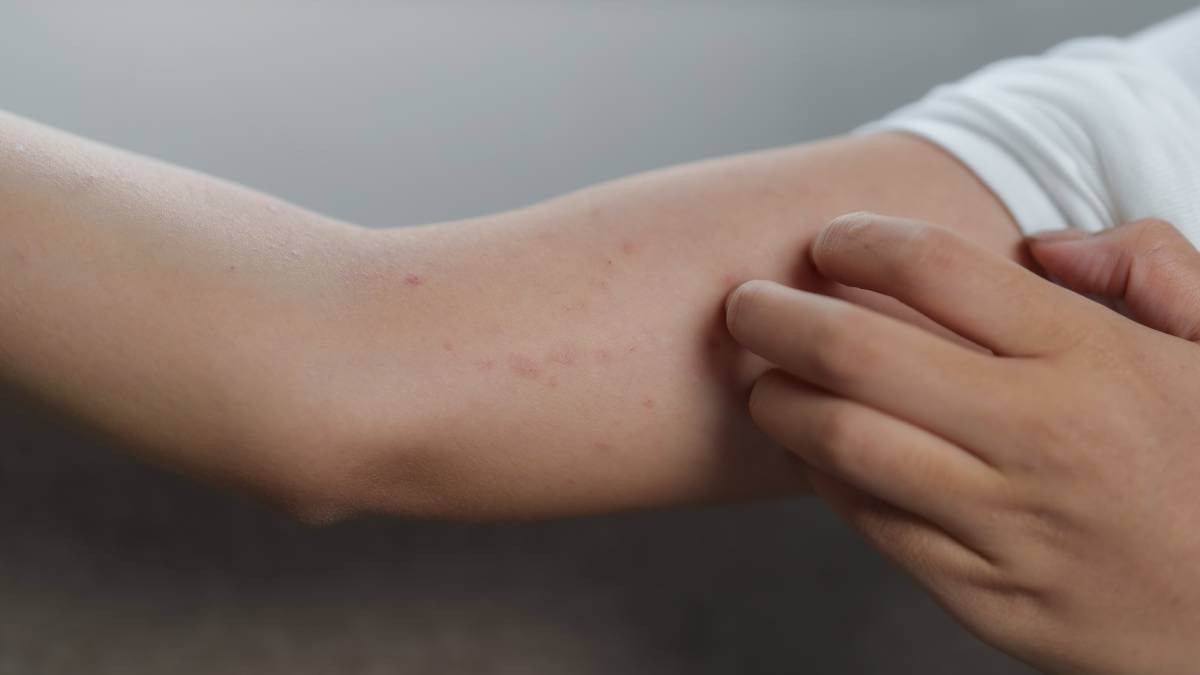
Allergic Reaction Anaphylaxis Symptoms
Anaphylaxis is a rapid and severe allergic reaction that can affect breathing, circulation, and consciousness. Recognising the warning signs quickly is critical; acting fast can save a life.
Key symptoms to watch for:
Airway & Breathing
- Trouble breathing, wheezing, or noisy breaths
- Persistent cough or a hoarse voice
- Swelling of the tongue or throat
- Feeling like the throat is closing or being “choked”
Circulation & Consciousness
- Sudden dizziness, feeling faint, or collapsing
- Pale, blue, grey, or clammy skin
- Confusion, disorientation, or extreme tiredness
Skin
- Red, raised, itchy rash (hives)
- Flushed or unusually pale skin
Gastrointestinal
- Stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhoea
Emergency actions:
- Use adrenaline immediately if the person has an auto-injector (EpiPen)
- Call 999 for emergency medical assistance
- Position the person safely: Lie them flat with legs slightly raised, unless they are struggling to breathe or vomiting, in which case, sit them up a little
- Stay calm and monitor their breathing, pulse, and level of consciousness until help arrives
Recognising the warning signs early can save lives. The Mayo Clinic guide on anaphylaxis explains what to do in severe allergic reactions.
5 Stages Of An Allergic Reaction
Knowing the stages of an allergic reaction can help you understand what’s happening in the body and respond quickly and effectively.
- Sensitisation: The first time your body encounters an allergen, it may not react immediately. Instead, your immune system starts producing specific antibodies to recognise this substance in the future
- Activation: On the next exposure, your immune cells (mast cells) spring into action, releasing chemicals like histamine. This triggers the allergic reaction and the familiar symptoms you might recognise
- Early-Phase Reaction (Minutes): Symptoms often appear quickly, sometimes within minutes. You may notice itching, hives, redness, sneezing, or wheezing as the body responds
- Late-Phase Reaction (Hours Later): Even after initial symptoms settle, inflammation can return hours later. This might cause renewed redness, swelling, or tightening of the airways, making it important to keep monitoring the person affected
- Resolution / Anaphylaxis: Mild reactions usually calm down on their own. However, severe, systemic reactions can develop, affecting breathing, circulation, and blood pressure. In these cases, immediate use of adrenaline (EpiPen) and emergency medical care is essential
How Long Do Allergic Reactions Last?
The duration of an allergic reaction can vary widely, depending on the allergen, how severe the reaction is, and the treatment used. Some reactions may pass within minutes, while others can last for days or even weeks.
Mild reactions:
- Food allergies: Often settle within a few hours, though mild symptoms like itching or a rash may linger
- Hives (Urticaria): Can appear suddenly and may last for hours, or come and go over several days or weeks
- Hay fever / pollen allergies: Symptoms can persist as long as you’re exposed to pollen or other environmental triggers
- Contact dermatitis: Reactions from things like metals, cosmetics, or plants may take a few days to appear and can take weeks to fully clear
Severe reactions (Anaphylaxis):
- Symptoms can come on rapidly, including breathing difficulties, dizziness, or anxiety
- With treatment, such as adrenaline (EpiPen), symptoms may improve within 30 minutes, but full recovery can still take several days
Factors that affect how long a reaction lasts:
- Severity: Mild vs. severe reactions will naturally last different lengths of time
- Exposure: Continued contact with the allergen can prolong symptoms
- Treatment: Taking antihistamines for mild reactions or using adrenaline for severe reactions can significantly influence recovery time
- Individual immune response: Everyone’s body reacts differently, so recovery times can vary
Understanding how long symptoms may last helps you stay prepared and monitor the person affected, ensuring they get the right care when needed.
How To Handle An Allergic Reaction
Knowing how to respond to an allergic reaction can make a real difference. The steps you take depend on whether the reaction is mild or more severe.
For mild to moderate reactions:
- Take an antihistamine: Oral medications such as cetirizine or loratadine can help relieve itching, hives, or sneezing. They work quickly to ease discomfort
- Soothe the skin: Apply a steroid cream to rashes or insect bites to reduce redness, swelling, and irritation
- Use a reliever inhaler if needed: For mild wheezing, take your prescribed inhaler, like salbutamol, to help open the airways
- Remove the trigger: Stop contact with whatever caused the reaction, whether it’s a food, insect, or something in the environment
- Keep a close watch: Even mild reactions can get worse, so monitor symptoms and seek medical advice if anything changes or doesn’t improve
For severe reactions (Anaphylaxis):
- Use adrenaline immediately: Apply the auto-injector (EpiPen) to the outer thigh as soon as possible
- Call emergency services (999): Explain that you suspect anaphylaxis, so help can arrive quickly
- Position the person safely: Have them lie flat with legs slightly raised. If they’re struggling to breathe, let them sit up a little. Pregnant individuals should lie on their left side
- Second dose if needed: If symptoms don’t improve after 5–10 minutes and another injector is available, use it
- Do not give food or drink: Avoid letting the person stand or walk
- Start CPR if necessary: If they stop breathing or lose consciousness, begin chest compressions until paramedics arrive
Reacting quickly and calmly is key; even a few minutes can make a big difference in keeping someone safe. For additional advice on treating allergic reactions safely at home, the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology provides helpful guidance on symptom management and prevention strategies.

When To Call An Ambulance For An Allergic Reaction
Call 999 immediately if:
- Lips, mouth, throat, or tongue swell suddenly
- Difficulty breathing, wheezing, or choking
- Throat feels tight, or swallowing is hard
- Skin, tongue, or lips turn blue, grey, or pale
- Sudden confusion, drowsiness, or dizziness
- Someone faints and cannot be woken
- A child is limp, floppy, or unresponsive
These may be signs of a serious allergic reaction requiring urgent hospital care.
Stay Prepared With Medic 365
Recognising the symptoms of an allergic reaction early and responding appropriately can save lives. With our first aid at work courses in Milton Keynes, Medic 365 equips you with practical skills, confidence, and peace of mind. Our courses cover allergic reactions, CPR, and emergency response techniques, tailored to workplaces, schools, and community settings.
Investing in proper training ensures you’re ready to act safely and effectively, helping you protect those around you when seconds count. Contact us to learn more.